Cloning history / Cloning strategy#
When using pydna to plan cloning, it stores the provenance of Dseqrecord objects in
their source attribute. Not all methods generate sources so far, so refer to the documentation
notebooks for examples on how to use this feature. The history method of Dseqrecord objects
can be used to get a string representation of the provenance of the sequence. You can also
use the CloningStrategy class to create a JSON representation of the cloning strategy.
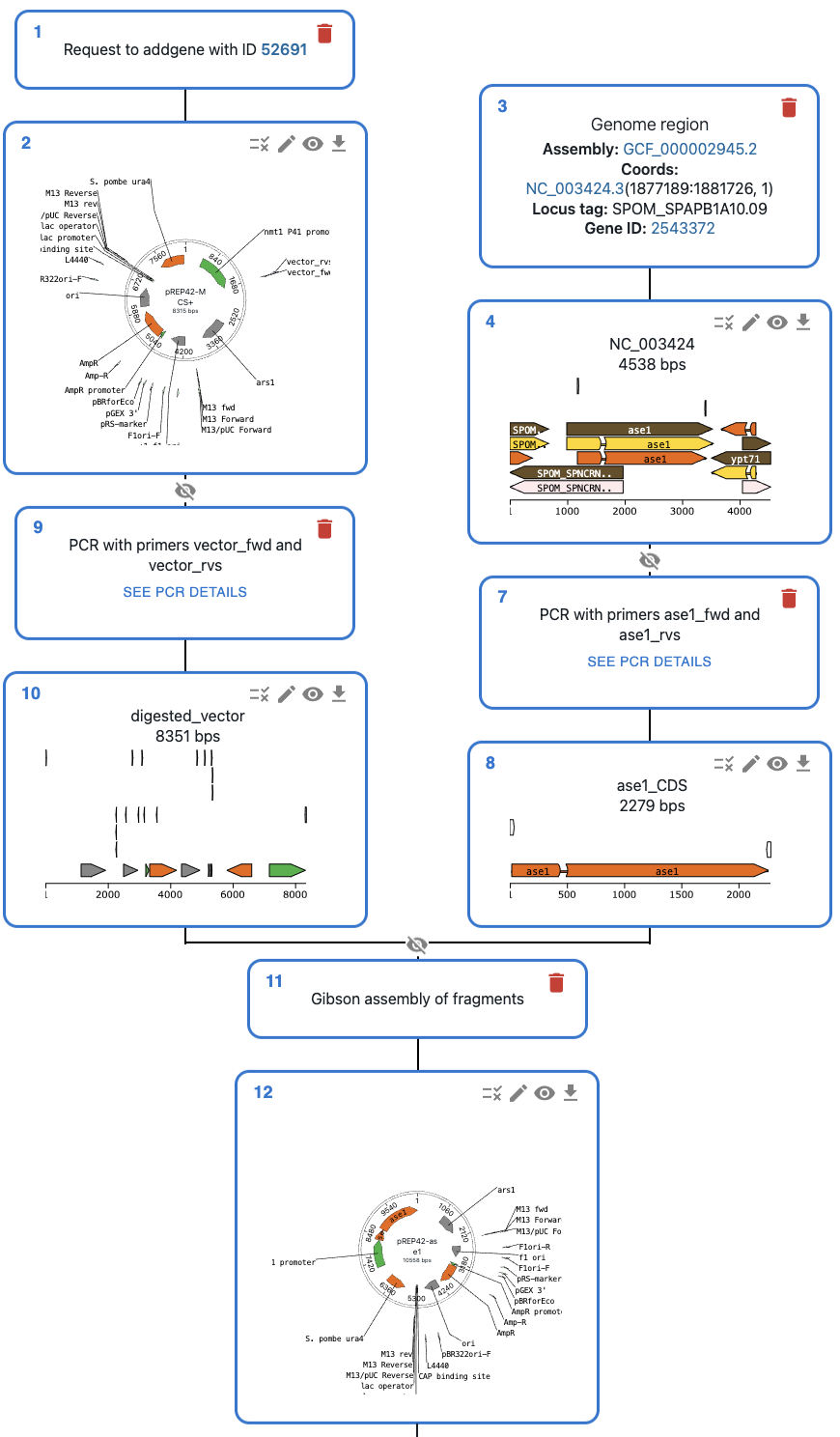
That CloningStrategy can be loaded in the OpenCloning web interface to see a representation
of the cloning strategy like below. See an example in this link.
%%capture
# Install pydna (only when running on Colab)
import sys
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules:
# Install the last version of pydna
%pip install "git+https://github.com/pydna-group/pydna.git"
# Use curl to get the files for gateway:
!curl -LO "https://github.com/pydna-group/pydna/raw/master/tests/gateway_manual_cloning/pDONRtm221.dna"
!curl -LO "https://github.com/pydna-group/pydna/raw/master/tests/gateway_manual_cloning/pcr_product-attP1_1-attP2_1.dna"
!curl -LO "https://github.com/pydna-group/pydna/raw/master/tests/gateway_manual_cloning/pET-53-DESTtm.dna"
import os
from pydna.dseqrecord import Dseqrecord
from pydna.assembly2 import (
golden_gate_assembly,
gibson_assembly,
ligation_assembly,
gateway_assembly,
homologous_recombination_integration,
homologous_recombination_excision,
cre_lox_integration,
cre_lox_excision,
pcr_assembly,
crispr_integration,
)
from Bio.Restriction import BsaI, EcoRI, SalI
from pydna.parsers import parse_snapgene
from pydna.opencloning_models import CloningStrategy
from pydna.primer import Primer
from Bio.Seq import reverse_complement
Golden Gate assembly (BsaI)#
This section assembles three inserts into a circular vector using Golden Gate with BsaI and exports the design as JSON.
insert1 = Dseqrecord("GGTCTCAattaAAAAAttaaAGAGACC", name="insert1")
insert2 = Dseqrecord("GGTCTCAttaaCCCCCatatAGAGACC", name="insert2")
insert3 = Dseqrecord("GGTCTCAatatGGGGGccggAGAGACC", name="insert3")
vector = Dseqrecord("TTTTattaAGAGACCTTTTTGGTCTCAccggTTTT", circular=True, name="vector")
product, *_ = golden_gate_assembly(
[insert1, insert2, insert3, vector], [BsaI], circular_only=True
)
product.name = "product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([product])
with open("golden_gate.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(product.history())
╙── product (Dseqrecord(o39))
└─╼ RestrictionAndLigationSource
├─╼ insert1 (Dseqrecord(-27))
├─╼ insert2 (Dseqrecord(-27))
├─╼ insert3 (Dseqrecord(-27))
└─╼ vector (Dseqrecord(o35))
Gibson assembly#
This section assembles three linear fragments using Gibson assembly and serializes the resulting product to JSON.
fragments = [
Dseqrecord("TTTTacgatAAtgctccCCCC", circular=False, name="fragment1"),
Dseqrecord("CCCCtcatGGGG", circular=False, name="fragment2"),
Dseqrecord("GGGGatataTTTT", circular=False, name="fragment3"),
]
product, *_ = gibson_assembly(fragments, limit=4)
product.name = "product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([product])
with open("gibson.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(product.history())
╙── product (Dseqrecord(o34))
└─╼ GibsonAssemblySource
├─╼ fragment1 (Dseqrecord(-21))
├─╼ fragment2 (Dseqrecord(-12))
└─╼ fragment3 (Dseqrecord(-13))
Restriction, then ligation assembly (EcoRI/SalI)#
This section cuts a template with EcoRI and SalI, ligates compatible fragments, and exports the result as JSON.
a = Dseqrecord("aaGAATTCccGTCGACaa")
c, d, e = a.cut(EcoRI, SalI)
product, *_ = ligation_assembly([c, d, e])
a.name = "a"
c.name = "c"
d.name = "d"
e.name = "e"
product.name = "product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([product])
with open("restriction_ligation.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(product.history())
╙── product (Dseqrecord(-18))
└─╼ LigationSource
├─╼ c (Dseqrecord(-7))
│ └─╼ RestrictionEnzymeDigestionSource
│ └─╼ a (Dseqrecord(-18)) ╾ RestrictionEnzymeDigestionSource, RestrictionEnzymeDigestionSource
├─╼ d (Dseqrecord(-12))
│ └─╼ RestrictionEnzymeDigestionSource
│ └─╼ ...
└─╼ e (Dseqrecord(-7))
└─╼ RestrictionEnzymeDigestionSource
└─╼ ...
Gateway assembly (BP and LR)#
This section creates an Entry vector via BP reaction, then generates an Expression clone via LR reaction using test SnapGene files.
if 'google.colab' in sys.modules:
files_path = ""
else:
files_path = "../../tests/gateway_manual_cloning"
line = "pDONRtm221.dna pcr_product-attP1_1-attP2_1.dna entry-attP1_1-attP2_1.dna pET-53-DESTtm.dna expression-attP1_1-attP2_1.dna".split(
"\t"
)
backbone, pcr_product, _, backbone_expression, _ = line
backbone = parse_snapgene(os.path.join(files_path, backbone))[0]
pcr_product = parse_snapgene(os.path.join(files_path, pcr_product))[0]
backbone_expression = parse_snapgene(os.path.join(files_path, backbone_expression))[0]
# Works with the right reaction
entry_vector = gateway_assembly(
[backbone, pcr_product], "BP", multi_site_only=True, circular_only=True
)[0]
expression_clone, _ = gateway_assembly(
[backbone_expression, entry_vector], "LR", multi_site_only=True, circular_only=True
)
expression_clone.name = "expression_clone"
backbone_expression.name = "backbone_expression"
entry_vector.name = "entry_vector"
backbone.name = "backbone"
pcr_product.name = "pcr_product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([expression_clone])
with open("gateway.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(expression_clone.history())
╙── expression_clone (Dseqrecord(o7423))
└─╼ GatewaySource
├─╼ backbone_expression (Dseqrecord(o6832))
│ └─╼ UploadedFileSource
└─╼ entry_vector (Dseqrecord(o4790))
└─╼ GatewaySource
├─╼ backbone (Dseqrecord(o4761))
│ └─╼ UploadedFileSource
└─╼ pcr_product (Dseqrecord(-2304))
└─╼ UploadedFileSource
Homologous recombination integration#
This section performs homologous recombination integration of two inserts into a genome and exports the result as JSON.
homology = "AAGTCCGTTCGTTTTACCTG"
genome = Dseqrecord(f"aaaaaa{homology}ccccc{homology}aaaaaa")
insert = Dseqrecord(f"{homology}gggg{homology}")
integration_product, *_ = homologous_recombination_integration(genome, [insert], 20)
excision_product, *_ = homologous_recombination_excision(integration_product, 20)
genome.name = "genome"
insert.name = "insert"
integration_product.name = "integration_product"
excision_product.name = "excision_product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([excision_product])
with open("homologous_recombination.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(excision_product.history())
╙── excision_product (Dseqrecord(o24))
└─╼ HomologousRecombinationSource
└─╼ integration_product (Dseqrecord(-56))
└─╼ HomologousRecombinationSource
├─╼ genome (Dseqrecord(-57))
└─╼ insert (Dseqrecord(-44))
Cre-lox integration#
This section performs Cre-lox integration , then excision.
from pydna.cre_lox import LOXP_SEQUENCE
a = Dseqrecord(f"cccccc{LOXP_SEQUENCE}aaaaa")
b = Dseqrecord(f"{LOXP_SEQUENCE}bbbbb", circular=True)
integration_product, *_ = cre_lox_integration(a, [b])
excision_product, *_ = cre_lox_excision(integration_product)
a.name = "genome"
b.name = "plasmid"
integration_product.name = "integration_product"
excision_product.name = "excision_product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([excision_product])
with open("cre_lox.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(excision_product.history())
╙── excision_product (Dseqrecord(o39))
└─╼ CreLoxRecombinationSource
└─╼ integration_product (Dseqrecord(-84))
└─╼ CreLoxRecombinationSource
├─╼ genome (Dseqrecord(-45))
└─╼ plasmid (Dseqrecord(o39))
PCR assembly#
This section performs PCR assembly and exports the result as JSON.
primer1 = Primer("ACGTACGT")
primer2 = Primer(reverse_complement("GCGCGCGC"))
seq = Dseqrecord("ccccACGTACGTAAAAAAGCGCGCGCcccc")
product, *_ = pcr_assembly(seq, primer1, primer2, limit=8)
primer1.name = "primer1"
primer2.name = "primer2"
seq.name = "seq"
product.name = "product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([product])
with open("pcr.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(product.history())
╙── product (Dseqrecord(-22))
└─╼ PCRSource
├─╼ primer1 (id 8-mer:5'-ACGTACGT-3')
├─╼ seq (Dseqrecord(-30))
└─╼ primer2 (id 8-mer:5'-GCGCGCGC-3')
CRISPR integration#
Works like homologous recombination, but takes a list of guides and inserts. The guides must be primers
genome = Dseqrecord("aaccggttcaatgcaaacagtaatgatggatgacattcaaagcac", name="genome")
insert = Dseqrecord("aaccggttAAAAAAAAAttcaaagcac", name="insert")
guide = Primer("ttcaatgcaaacagtaatga", name="guide")
product, *_ = crispr_integration(genome, [insert], [guide], 8)
product.name = "product"
cs = CloningStrategy.from_dseqrecords([product])
with open("crispr.json", "w") as f:
f.write(cs.model_dump_json())
print(product.history())
╙── product (Dseqrecord(-27))
└─╼ CRISPRSource
├─╼ genome (Dseqrecord(-45))
├─╼ insert (Dseqrecord(-27))
└─╼ guide (id 20-mer:5'-ttcaatgcaaacagtaatga-3')
